
It has a second ‘Samples” category to provide different sample results of one experiment group. The one from Jan Pieter allows category to make the box colorful.
What does a box and whisker plot show series#
In this chart, you have to explicitly say ‘Do not summarize’ in the Values bucket to view each series and data point. In Brad’s chart, every data point is plotted as a circle on the axis this lets us visualize the distribution of the data points, the top and bottom 5% as ‘outliers’ and color them red and mark the ‘whiskers’ at those points, the 95th quantile and the 5th quantile. You can also adjust these quantile values to meet your needs.

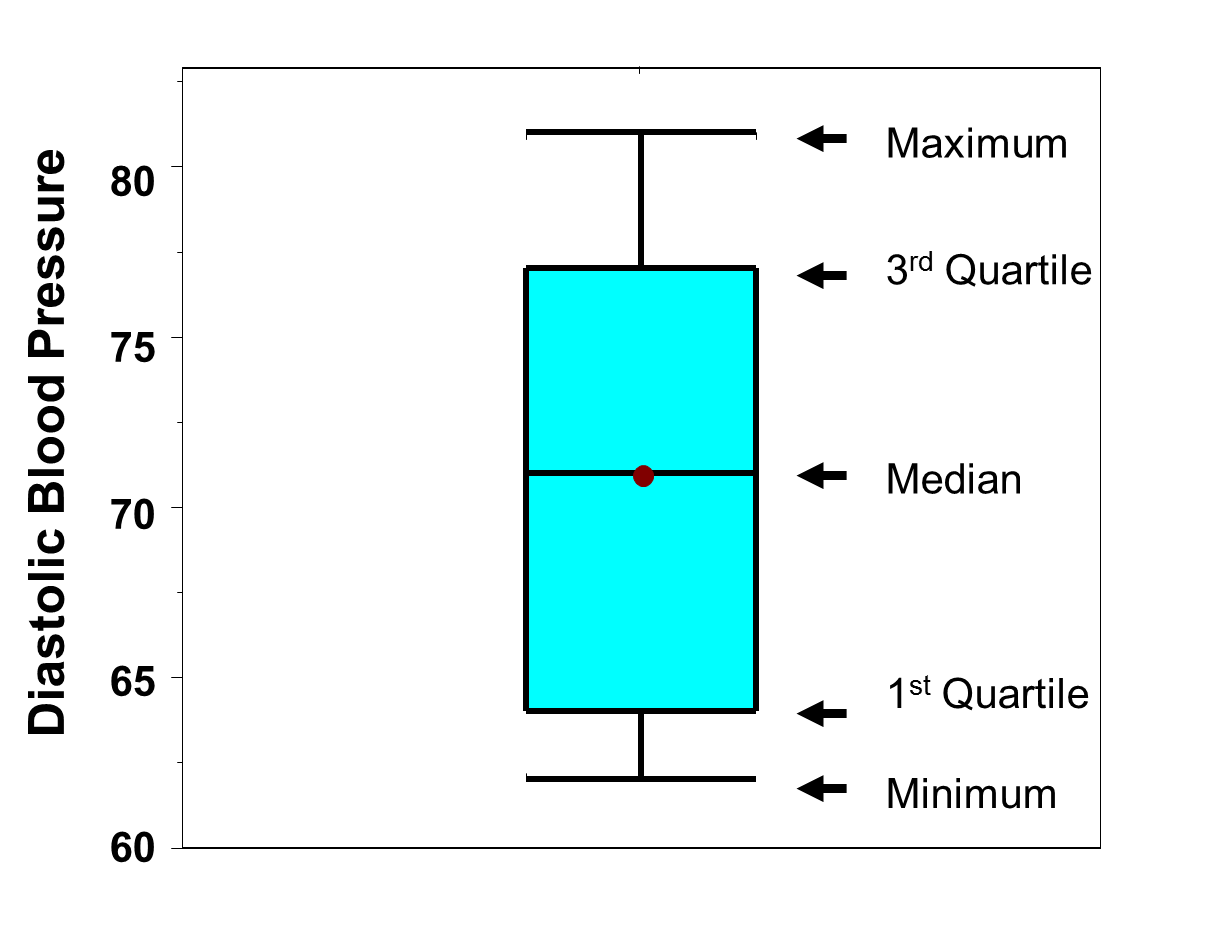
Thanks to both them for producing this very important visual and publishing it to the gallery. This week we have two submissions to the gallery about Box and Whisker – one from Brad Sarsfield and another from Jan Pieter Posthuma. If a data value is very far away from the quartiles (either much less than Q1 or much greater than Q3 ), it is sometimes designated an outlier. This summary approach allows the viewer to easily recognize differences between distributions and see beyond a standard mean value plots. A box whisker plot uses simple glyphs that summarize a quantitative distribution with: the smallest and largest values, lower quantile, median, upper quantile. We can see outliers, clusters of data points, different volume of data points between series all things that summary statistics can hide. A box plot is a good way to get an overall picture of the data set in a compact manner. It is called Q 0 because it is the 0 th quartile. The box whisker plot allows us to see a number of different things in the data series more deeply. The box-whisker plot (or a boxplot) is a quick and easy way to visualize complex data where you have multiple samples. A box plot (sometimes called a box and whisker plot) shows these five statistics: Minimum (Q0) this is the lowest value in the data set (0 th percentile ). Select the data you want to use to make the chart. This can be a single data series or multiple data series.

Enter the data you want to use to create a box and whisker chart into columns and rows on the worksheet. In his words, the greatest value of a picture is when it forces us to notice what we never expected to see and box plot does it perfectly. For Excel 2019, Excel 2016, or Excel for Microsoft 365, make a box and whisker plot chart using the Insert Chart tool. Half a century ago, one mathematician thought out-of-the-box, to solve this problem and came up with the box plot. This is also where other metrics come into play, like the median, 95 percentiles that can give us a better understanding of the data. Now we may be happy with that metric, but what happens if every now and then it takes 6000ms to load? The 300ms average number hides that alarmingly bad experience for sizable customer base. What if sizable number of customers are experiencing a slow load time even though the average is within the limits of our expectation? Imagine that we had a dataset that showed on average it took 300ms to load the app. The bottom of the box is the first quartile (25th percentile) and. While the average is often a useful metric, by itself is a lossy compression algorithm. The box represents the middle 50 of observed values. Showing averages over time or across some series of data often allows us to answer questions like: How long did the app take to load in the mobile device? To answer this question, most commonly, we would find all data points for the day and then compute the average. But when you have diverse data points and sources, telling the story with just one aggregation to represent the whole range of numbers might often not tell the fully story. The single points on the diagram show the outliers.By Amir Netz, Technical Fellow and Mey Meenakshisundaram, Product Manager The values at which the horizontal lines stop at are the values of the upper and lower values of the data. The right edge of the box shows the upper quartile it shows that $25$% of the data lies to the right of the upper quartile value. The left edge of the box represents the lower quartile it shows the value at which the first $25$% of the data falls up to. This shows that $50$% of the data lies on the left hand side of the median value and $50$% lies on the right hand side. The line splitting the box in two represents the median value. Interpreting a boxplot can be done once you understand what the different lines mean on a box and whisker diagram. These can be displayed alongside a number line, horizontally or vertically. It is a useful way to compare different sets of data as you can draw more than one boxplot per graph. The shape of the boxplot shows how the data is distributed and it also shows any outliers. Contents Toggle Main Menu 1 Definition 2 Reading a Box and Whisker Plot 2.1 Video Examples 3 Constructing a Box and Whisker Diagram 4 Worked Example 4.1 Video Example 4.2 Common Mistakes 5 Workbook 6 Test Yourself 7 External Resources DefinitionĪ box and whisker plot or diagram (otherwise known as a boxplot), is a graph summarising a set of data.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
